The automobile industry has seen many advancements over the years, and one of these is the evolution of car alternators. In this article, we will take a look at how car alternators have changed over time, from their first introduction to present-day technology and future predictions about what they may become shortly.
Well, explore how car alternators work, what makes them so important for modern cars, and why they continue to be an integral part of automotive engineering. Finally, will examine some potential areas where further development could lead us in the coming years.
By examining all aspects of car alternators – past, present, and future – this article hopes to provide insight into their continuing importance for vehicle owners around the world.
The History of Car Alternators
The history of car alternators is as old as the automobile itself. Invented in 1836, they were originally used to power mechanical devices and eventually became an integral part of automotive technology. The first alternator was a dynamo powered by a gasoline engine which generated electricity for charging batteries and powering lights, ignition systems, and other accessories.
As cars began to use more electronics during the 1920s and 1930s, the need for better electrical power sources increased. By this time most vehicles had switched from dynamos to alternators due to their superior efficiency in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
For these early alternators to work properly they needed regulation circuits that would ensure their proper operation at all times regardless of engine speed or load demands on the system. Voltage regulators were developed over time that could be adjusted manually using potentiometers or automatically using electronic feedback control systems such as those found in modern automobiles today.
By mid-century advances in materials science allowed large-scale production of lightweight aluminum alloy construction parts which enabled efficient manufacturing techniques leading to even greater gains in efficiency and reliability concerning car alternators compared with earlier models constructed from heavy steel components. This helped spur further development efforts resulting in higher output ratings while still maintaining small sizes suitable for installation within contemporary engine compartments where space was limited due to increasing component complexity demands made by ever-advancing safety standards and consumer expectations alike.
Today modern car alternator designs continue pushing boundaries thanks largely due advancements in computer-aided design software allowing engineers more flexibility when it comes to designing complex components like stators featuring multiple windings which help improve performance without sacrificing size or weight constraints dictated by current market trends emphasizing fuel economy above all else. Looking ahead we can expect continued progress towards lighter yet more powerful units capable of providing improved output characteristics while still consuming minimal amounts of energy from our already stretched resources making them essential elements not only for our present-day but also future generations looking forward to building upon existing technologies laid down before us now!
Projected Developments for the Future of Car Alternators
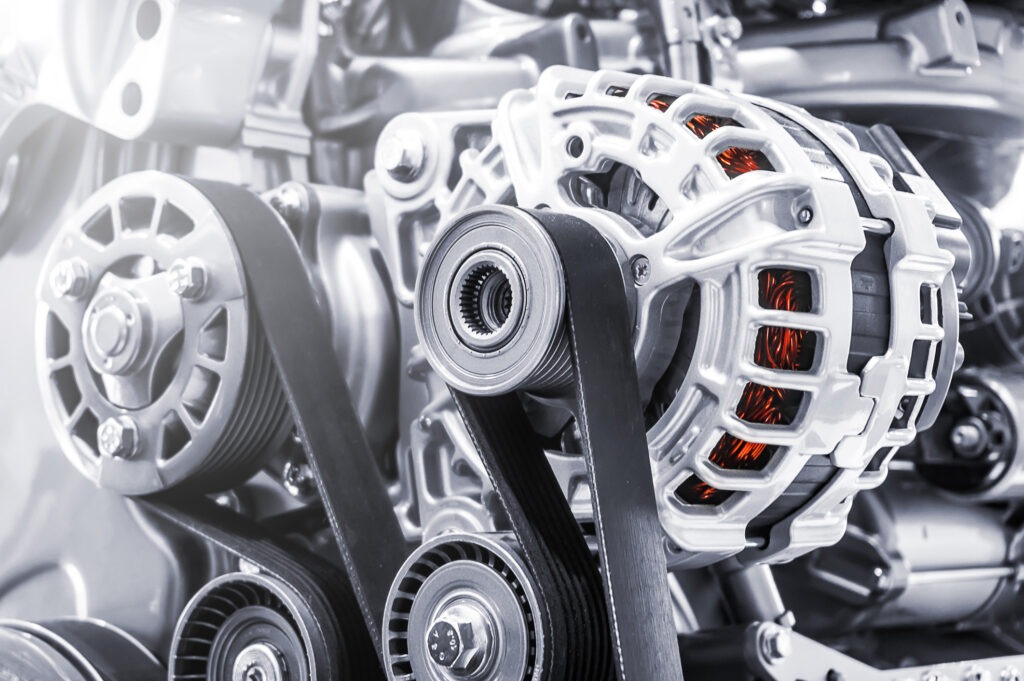
The future of car alternators is looking bright, with developments in technology leading to safer, more efficient models. Automakers are constantly striving for increased power output and improved fuel efficiency while still maintaining the highest safety standards.
As such, they are turning to advanced materials and processes such as nanotechnology and laser welding to create lighter yet powerful alternators that can withstand extreme temperatures and environmental conditions. With these innovations come smaller sizes, higher power outputs, and greater reliability.
Additionally, automakers are exploring new ways to reduce emissions by implementing hybrid systems or regenerative braking which harvests energy from the brakes when stopping a vehicle. Another projected development is an increase in automation within the automotive industry; self-driving cars will require highly accurate alternators that can process data quickly without sacrificing quality or performance.
This presents a challenge for manufacturers but could result in better overall driving experiences due to improved accuracy of navigation systems coupled with smoother engine operation through precise control over voltage settings during acceleration or deceleration phases of driving cycles. Finally, advancements in battery technology have opened up possibilities for electric vehicles powered solely by batteries rather than gasoline-powered engines requiring an alternator system at all – however, this does not mean that traditional alternator technology is becoming obsolete anytime soon since there will continue to be applications where it remains necessary even into the distant future.
Conclusion
The car alternator has come a long way in terms of innovation and advancement, from its roots as an early form of automotive charging system to the modern-day device that is capable of powering almost any electrical requirement within a vehicle. From past, present, and future predictions, it is clear that the car alternator will continue to be an integral part of cars for many more years to come.
As technology advances further so too does the car alternator with new features being developed all the time; ensuring vehicles are kept up-to-date with industry standards. The car alternators’ evolution over time has allowed us to have reliable and efficient power sources available for use in our cars today, and this trend should continue well into the future.